
WASHINGTON (AP) – Nearly a week before the Thanksgiving travel crush, federal air security officials were struggling to reassure rising numbers of fliers and airline workers outraged by new anti-terrorism screening procedures they consider invasive and harmful.
Across the country, passengers simmered over being forced to choose scans by full-body image detectors or probing pat-downs. Top federal security officials said Monday that the procedures were safe and necessary sacrifices to ward off terror attacks.
“It’s all about security,” Homeland Security Secretary Janet Napolitano said. “It’s all about everybody recognizing their role.”
Despite officials’ insistence that they had taken care to prepare the American flying public, the flurry of criticism from private citizens to airline pilots’ groups suggested that Napolitano and other federal officials had been caught off guard.
At the San Diego airport, a software engineer posted an Internet blog item saying he had been ejected after being threatened with a fine and lawsuit for refusing a groin check after turning down a full-body scan. The passenger, John Tyner, said he told a federal Transportation Security Administration worker, “If you touch my junk, I’m gonna have you arrested.”
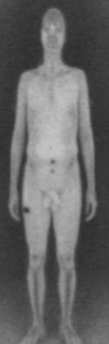
Tyner’s individual protest quickly became a web sensation, but questions also came from travel business groups, civil liberties activists and pilots, raising concerns both about the procedures themselves and about the possibility of delays caused by passengers reluctant to accept the new procedures.
“Almost to a person, travel managers are concerned that TSA is going too far and without proper procedures and sufficient oversight,” said Kevin Mitchell, chairman of the Business Travel Coalition, an advocacy group representing corporate travel departments. “Travel managers are hearing from their travelers about this virtually on a daily basis.”
Jeffrey Price, an aviation professor at Metropolitan State College of Denver, said two trends are converging: the regular holiday security increases and the addition of body scanners and new heightened measures stemming from the recent attempted cargo bombings. Also, several airports are short-staffed, which will add to delays, Price said.
Homeland Security and the TSA have moved forcefully to shift airport screening from familiar scanners to full-body detection machines. The new machines show the body’s contours on a computer stationed in a private room removed from the security checkpoints. A person’s face is never shown and the person’s identity is supposedly not known to the screener reviewing the computer images.
Concerns about privacy and low-level radiation emitted by the machines have led some passengers to refuse screening. Under TSA rules, those who decline must submit to rigorous pat-down inspections that include checks of the inside of travelers’ thighs and buttocks. The American Civil Liberties Union has denounced the machines as a “virtual strip search.”
Concerns about both procedures are not limited to the U.S. In Germany over the weekend, organized protesters stripped off their clothes in airports to voice their opposition to full-body scans.
Douglas R. Laird, a former security director for Northwest Airlines, said it’s the resistance to these measures that will cause the most delays. The new enhanced pat-downs, an alternative to body scanners, take more time – about 2 minutes compared with a 30-second scan. Delays could multiply if many travelers opt for a pat-down or contest certain new procedures.
Beyond the scanning process, passengers will also be subject to greater scrutiny of their luggage and personal identification and stricter enforcement of long-standing rules like the ban on carry-on liquids over 3 ounces.
On Monday, top security officials were out in force to defend the new policies. Napolitano wrote an op-ed piece in USA Today insisting that the body scanners used at many airports were safe and any images were viewed by federal airport workers in private settings.
Napolitano later said in a news conference at Ronald Reagan National Airport that she regretted the growing opposition to moves by the federal government to make flying safer. But she said the changes were necessary to deal with emerging terrorist threats such as a Nigerian man’s alleged attempt to blow up a jetliner bound from Amsterdam to Detroit last Christmas Day using hard-to-detect explosives. Authorities allege that the explosives were hidden in the suspect’s underwear.
There are some 300 full-body scanners now operational in 60 U.S. airports. TSA is on track to deploy approximately 500 units by the end of 2010.
Officials for the Airports Council International-North America, which represents U.S. and Canadian airports, said their members haven’t complained about the scanner and pat-down policy or reported any special problems. But airports have been urging the government to engage in an aggressive public education campaign regarding the new screening, said Debby McElroy, the council’s executive vice president.
“TSA is trying to address a real, credible threat, both through the advanced imaging technology and through the pat-downs,” McElroy said. “We think it’s important that they continue to address it with passengers and the media because there continues to be a significant misunderstanding about both the safety and the privacy concerns.”
A spokeswoman for American Airlines issued a carefully worded statement that stopped short of welcoming the government’s security moves. “We are working with the unions and the TSA and continue to evaluate and discuss screening options,” American spokeswoman Missy Latham said.
Some airline pilots have pushed back against the new rules screening them. Many pilots are already part of the Federal Flight Deck Officer Program, which trains pilots in the use of firearms and defensive tactics. They are permitted to carry weapons on board.
Pilots enrolled in the program don’t have to go through scanners and pat-downs. But only a small share of the total number of U.S. pilots are enrolled in the program.
Capt. John Prater, head of the Air Line Pilots Association, said based on discussions with TSA officials on Monday that he’s optimistic the agency will soon approve a “crew pass” system that allows flight attendants and pilots to undergo less-stringent screenings.
After the Sept. 11, 2001, terrorist attacks, pilot unions were shown an off-the-shelf biometric identification system that was ready to go by government officials, said Sam Mayer, a Boeing 767 captain and a spokesman for the Allied Pilots Association, which represents pilots at American Airlines. The system would have made screening pilots unnecessary, he said.
Nine years later, pilots still don’t have biometric identification cards because the government and airlines have been quarreling over who should pay for the machines that can read biometric information like fingerprints and iris scans, Mayer said.
“At the end of the day we’re not the threat, and we want the TSA to concentrate on getting bads guys,” he said.
Pilots are also concerned about the cumulative effects of radiation, Mayer said. Depending upon their schedules, pilots can go through a scanner several times a day and several days a week, he said.
“We’re already at the top of the radiation (exposure) charts to begin with because we’re flying at high altitudes for long distances,” Mayer said. “The cumulative effects of this are more than most pilots are willing to subject themselves to. We’re right up there with nuclear power plant workers in terms of exposure.”
—
Associated Press writers Samantha L. Bonkamp in New York, Sam Hananel in Washington, D.C., and Robert Jablon and Daisy Ngyuen in Los Angeles contributed to this report.
By JOAN LOWY and ADAM GOLDMAN

